
Mikhail Prokhorov: Business Tycoon to Billionaire President?
Mikhail Prokhorov is a tycoon in Russia, Jay-Z’s partner in Brooklyn—and a strong candidate to eventually replace Vladimir Putin in the Kremlin, a prospect the billionaire is turning into his full-time job
When billionaire Mikhail Prokhorov, alpha oligarch and partner of Jay-Z, comes to New York, he typically nabs the 52nd-floor penthouse suite at the top of the Four Seasons hotel in midtown Manhattan, which goes for $35,000 a night. It has nine rooms, and when I meet Prokhorov, he’s relaxing his 6-foot-8 frame on a couch in the dining area.
He’s in town in early February for just a couple of nights, as usual, to watch his Brooklyn Nets. Tonight they’re playing against the equally matched Chicago Bulls. Three years ago, he put $200 million into the Nets, which moved to the spectacular new Barclays Center last fall.
But the Nets are “a passion project”—more of a hobby than a serious preoccupation. “I have handed off all of my active business assets to my partners to manage,” says Prokhorov, “so that 100 percent of my time is devoted to politics.”
Sceptics may be forgiven the arched eyebrow. Prokhorov burst upon the Russian political scene just in time to run against strongman Vladimir Putin, whose 2012 election for a third term as president was a foregone conclusion. Before announcing his decision to run as an independent, Prokhorov surrendered his political party, Right Cause, to the Kremlin, saying that it was only a puppet of the government. At the same time, he negotiated with “the puppeteers”, who allowed him to run for president and collect 2 million necessary signatures in record time while other candidates were flailing. Attracting 8 percent of the vote in a third-place finish, Prokhorov went mute for a while after Putin returned to power.
The next time, he insists, he’s serious. “We are in the process of building a real, strong, powerful party called the Civic Platform. That’s what I do all day.”
To gain credibility, as well as traction, he must disprove the label of full-time dabbler. Now 47, Prokhorov has been, by turns, a hawker of denim, a banker, a metals mogul, an extreme athlete, a playboy, a sports team owner, a politician, a media power ... and a politician again. “I consider myself an alternative” to the current regime, he says. “I have, of course, already run for president. If the Civic Platform continues to move ahead, further participation in presidential elections is a possibility.” Prokhorov is careful to note his respect for Putin. But challenging the Kremlin in any way is still a dangerous game. Opponents like Prokhorov’s former oligarch contemporary, Mikhail Khodorkovsky, have found themselves entombed in the gulag. Others—like Alexander Litvinenko, ex-KGB agent-turned-MI6 spy, and Sergei Magnitsky, an accountant-turned-whistleblower—have ended up dead. (The Kremlin has denied any involvement in Litvinenko’s death.)
So Prokhorov is writing a new political playbook for billionaires, one far more complicated and high-stakes than the one Michael Bloomberg used to spend his way into Gracie Mansion or Silvio Berlusconi to leverage his media holdings to become Italy’s prime minister. He knows he can’t act too boldly or defiantly, or the Kremlin will shut him down immediately. He also knows he can’t be too closely allied with Putin, or he will lose credibility. And he can certainly read a calendar: The next presidential election is five years away. There’s a lot of groundwork that must be done, and Prokhorov, a consummate chess player as a kid, is suited to temporising and making thoughtful moves. “He knows how to calculate several steps ahead and can think about several things at the same time,” says Yevgeny Roizman, who followed Prokhorov from Right Cause to Civic Platform. With a net worth of $13 billion, Prokhorov can hang in this game a while.
As for tonight’s game, Prokhorov, who has changed into a trim gray suit, monogrammed white shirt and blue tie, takes a limo to Brooklyn. We cross the East River and head down Atlantic Avenue to Barclays Center. A car elevator dumps Prokhorov in the centre of the building. On the way to his private box, he is mobbed by strangers. Prokhorov waves, shakes hands, promises two kids in Nets jerseys he’ll give them an autograph later. “You’ve put your tie on! Do I need a tie now?” asks his partner in the Brooklyn venture, real estate developer Bruce Ratner, who pulls a cravat out of his own jacket pocket and playfully waves it in the air.
Ratner is the main force behind the once controversial arena and a 55-45 owner of it with Prokhorov. The two are partners in the Nets as well (Prokhorov: 80 percent; Ratner: 20 percent). The third member of an odd trio is hip-hop sensation Jay-Z, who performed at the opening of the centre last September. (He has a reported cut of the action.) Or maybe not so odd: They’re all self-made, outsize successes. Prokhorov says there is “a natural bond” between him and Jay-Z. Not incidentally, high-profile friends like these in America’s media capital provide a kind of insurance, given the political risks he is embracing. Virtually no New Yorkers can name Khodorkovsky, much less rally around the absurd injustice that has befallen him and his cause; Prokhorov is now far more visible.
As the game starts, Prokhorov sits down with Mila, an “acquaintance” who, he later admits, was an ex-girlfriend, and a smattering of Russians from his US-based Onexim Sports & Entertainment. Prokhorov watches the game nervously, fidgeting, cracking his knuckles and, when Chicago takes the ball up-court, roaring, “Those SOBs will now score!” For him, though, it’s simply “a way of relaxing, if you will, a contrast to the headaches of political life”. Which says as much about Russian politics as it does about Prokhorov.
Prokhorov grew up side-stepping politics, if he thought about affairs of state at all. The now-familiar trajectory of his spectacular success—from student to banker to mining übercapitalist—depended on maintaining smooth relations with the government, first under the chaotic and corrupt mess of the Yeltsin administration, then under the increasingly repressive (if more orderly) but still corrupt Putin reign.
“He was not a troublemaker as a child,” says Prokhorov’s sister, Irina, 57. Reared in a well-educated Moscow family, Prokhorov learned about the world outside the Iron Curtain from his father, who travelled widely for the Soviet sports committee. Neither he nor Prokhorov’s mother, an engineer, lived to see the empire collapse; both were dead by 1989. At the time, after a two-year interruption in his studies to serve in the Soviet Army, Prokhorov was finishing his studies at the Moscow Finance Institute. Almost overnight, he morphed from a carefree little brother to the family breadwinner, says Irina, who was then divorced and had a young daughter. “All those precious things of student life—dating, romances, everything that most people experience during that time—he, unfortunately, missed out on.”
Becoming an entrepreneur was partly the result of having to support his family. (And a family it remains: He and Irina share a mansion outside of Moscow.) But Prokhorov ultimately sees it as a long-established pattern of risk-taking, starting with a stonewashed jeans business. “People would say to me, ‘What are you doing? You have a brilliant career ahead of you, and you’re throwing it away! This fad will end in two or three years.’ ”
Prokhorov didn’t stick around long enough to find out. His elite financial education helped him climb the ranks at an international bank that dealt with the former Soviet bloc and then move to another financial institution that was acquiring state assets by the hundred-million-dollar fistfuls. He hit true pay dirt when he and Vladimir Potanin, now a fellow billionaire, formed Onexim Bank, which handled loans to the government and treasury obligations, then dealt with bankrupt state enterprises. “People would say to me, ‘What are you doing?! Your own bank?! That’s so unreliable!’ ” Prokhorov recalls.
In fact, it was the quickest route to questionable riches in the mid- to late 1990s, during Russia’s often shady privatisation. Onexim was right in the middle of it all—supervising the auctions that gave it and other banks the right to lend to the government, which, in turn, collateralised those loans with shares of newly private companies. When the government defaulted on the loans, the banks acquired the shares. In late 1995, Onexim got control of Norilsk Nickel—the foundation of phenomenal wealth for both Prokhorov and Potanin, who later briefly served in a government post in charge of privatisation.
Prokhorov was good. He poured resources into Norilsk, made it a model of efficiency and turned it into a powerhouse. But he was also cocky—and lucky.
Cocky, as in the well-worn episode of being detained on a 2007 skiing vacation in the French Alps on suspicion of hiring hookers for his friends. He was cleared two years later and in 2011 was awarded France’s Legion of Honour. Still, the scandal lingers, along with rumours that variously portray Prokhorov as a pimp and the prostitutes as babysitters who read Turgenev classics as bedtime stories. “I go to nightclubs once every three weeks,” Prokhorov now shrugs. “I have lady fans; why hide it?”
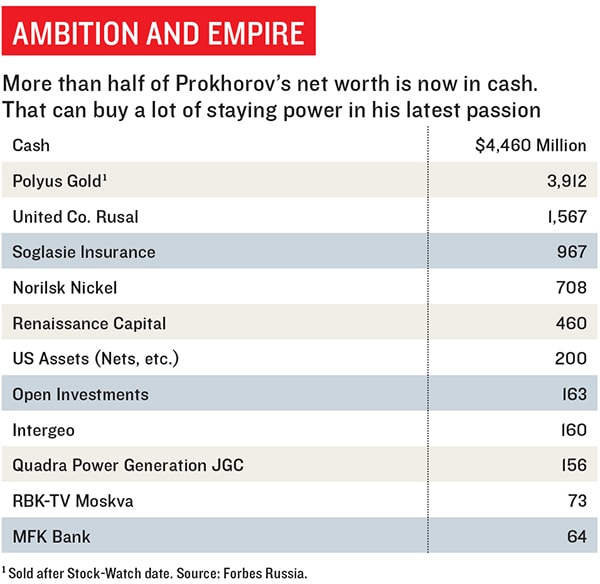
Lucky in his timing, Prokhorov cashed out of some of his mining, metals and energy interests between 2007 and 2008, just ahead of the financial crisis and the plunge in oil prices. (His net worth has since taken a 33 percent hit.) Onexim Group, his private investment fund, reaches into mining, metals, financial services, tech and media. But Prokhorov turned over day-to-day management to others last fall to concentrate full-time on politics. He recently sold off his biggest Russian asset, his 38 percent stake in Polyus Gold, for $3.6 billion. That’s on top of the $4.5 billion in cash that he presumably keeps outside of Russia—and out of the grasp of Kremlin meddlers.
Three years ago, it would have been hard to imagine Prokhorov’s running for office. Politics, he now claims in an eloquent but hardly off-the-cuff peroration, is the natural culmination of his life. “At a certain point, you begin to understand that at first, you’re in it for yourself—to provide financially for yourself, your family and your friends. Then you begin to realise that what you’re really proud of is not what you have achieved yourself but of those colleagues who have achieved success alongside you. Then, once you begin to manage large systems, you realise that business changes your life,” he says. “When you have gained a certain amount of experience, you find that a desire to help all people arises in you. How do you help all people? Through politics.”
Cut through the campaignspeak and a new kind of Russian politician begins to emerge: An intelligent, educated, successful, worldly guy who understands the value of competition—and isn’t tainted by a KGB past. Rich in resources and education, Russia is still in thrall to an autocrat and outdated political and economic institutions. “The world is changing fundamentally,” says Prokhorov. “Any country that is not up-to-date is in a great deal of danger—and Russia is one such country.”
The World Bank ranks it number 112, out of 185 nations, for ease of doing business. Transparency Inter- national’s Corruption Perceptions Index gives Russia a score of 28 out of a possible 100. Yet, there are more than stirrings of a middle class. Feeling marginalised and furious, the nation’s young and Moscow’s intelligentsia are bellowing for change.
What can Prokhorov offer? “He’s not going to create the revolution; he’ll wait for others to do it for him,” says Olga Khvostunova, research fellow at the Institute of Modern Russia, a pro-democracy organisation in Sparta, New Jersey. “And he will have a well-prepared party with a solid platform.”
Formed last summer, Civic Plat- form is still gelling. Last October it held a convention and spelled out its programme, which is fairly radical but regional in focus, at least initially. Prokhorov suggested changing the constitution to redraw Russia’s boundaries to end ethnic districts and republics. The party agreed to focus on upcoming gubernatorial elections, finding candidates in regions where Putin hasn’t claimed the privilege of appointing them. Civic Platform will also sweep in political activists drawn throughout the nation.
Hardly the stuff of Danton or Lenin. “This all seems very cautionary and more oriented towards building up [his political] presence, rather than establishing a long-term vision that people can follow,” says Mikhail Khodorkovsky’s son, Pavel. The older Khodorkovsky, once one of the world’s wealthiest men, crashed and burned when he engaged in politics and challenged Putin. He’s spent the last decade rotting in prison on highly questionable charges of tax evasion and embezzlement, with Yukos, his former oil empire, dismembered and largely renationalised.
Since last year’s presidential race, Putin has further tightened the screws against the opposition, marginalising or jailing the likes of dissident blogger Alexei Navalny and human rights activist Sergei Udaltsov. Civic Platform no doubt exists at the pleasure of Putin.
While Prokhorov deliberately calls himself a political “alternative”, rather than an opponent, he and Putin don’t see eye-to-eye at all about where Russia is headed. “Our views about the country’s further development differ,” Prokhorov says. “To me, personally, the individual is more important than the government. The government has to do everything in order to protect private property and individual freedom.”
The earmarks of a Prokhorov-backed platform are emerging: Western-leaning, pushing free markets, free speech and financial transparency. “We want to bring back political competition that will create a competitive economy,” says Yevgeny Roizman.
Prokhorov’s party is fielding candidates for an escalating series of contests: Regional elections; Moscow’s mayoral elections in 2015; Russia’s State Duma (parliament) elections in 2016; the race for president in 2018. “There is a lot of invisible but productive work being done to create the network the party will rely on later,” says Prokhorov. “We are in the so-called organisational stage, which is very, very important for future victories.”
There is also the task of re-introducing a billionaire as a serious political force to a cynical public. Many in the Russian liberal elite see the Civic Platform as a Kremlin- backed ploy to capture angry and alienated voters and politicians, says Alexander Kynev, a political analyst at a Moscow think tank. Prokhorov, he adds, “can be viewed as a candidate for some position in power”, and could be appointed to a government post in order to make unpopular decisions.
Prokhorov knows he has a high credibility hurdle. “If you don’t lie to people and you are honest and clear about how you made your money, you can look people in the eye and explain it to them,” he says. And you can promise them—credibly—that once you take office, you won’t have your hand in the till, “because stealing has become a very painful irritant for our citizens”.
So, in some quarters, has the constant demonising of America. “When there is little between two countries economically and their entire relationship rests on politics, this is an extremely unstable situation,” says Prokhorov, who sees a bridge between the two countries in sports and culture (his foundation, run by his sister, gave $1 million to the Brooklyn Academy of Music last September). “Unfortunately, in Russian history, the most effective method has always been to look for enemies. Well, I want to make us as many friends as possible.”
His friends in America seem convinced: “I don’t know the politics in Russia,” says Ratner. “But Mikhail has tremendous leadership skills. He’s very smart, has a sense of humour and he’s not afraid to make decisions—like Michael Bloomberg.” Nets swing- man Jerry Stackhouse, a 17-year veteran who has played for eight different franchises, sees it similarly, voicing respect for a person he sees as determined to make whatever changes are necessary, including a recent coaching replacement, to “get it right”. “He’s an owner that’s not concerned about anything but building a winner, building a champion.” A determined mindset as potent in politics as it is in basketball.
(This story appears in the 30 November, -0001 issue of Forbes India. To visit our Archives, click here.)







