
The Brewing of Sierra Nevada
Decades before the boutique beer boom Ken Grossman tasted opportunity. Sierra Nevada is now a juggernaut—and he might be worth $800 million
Ken Grossman has survived his share of froth and burst bubbles in the 35-plus years since he co-founded Sierra Nevada Brewing Co. Now 59, he still oversees the nation’s largest private craft brewery, producing nearly 1 million barrels of beer a year and ringing up more than $200 million in sales. Leaning back in his office chair, dressed in a plaid shirt and black zip-up vest and surrounded by empty beer bottles and photos of grandkids, Grossman seems the very image of a self-satisfied patriarch.
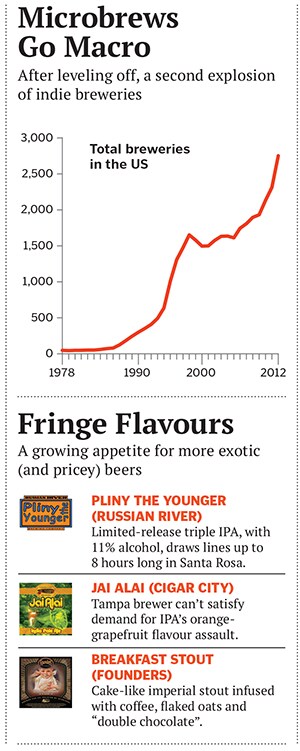
He’s not. Back in 1978, when Sierra Nevada was created, there were only 45 independent breweries in America. Today the $100-billion-a-year industry (US sales) is dominated by the likes of Anheuser-Busch InBev and MillerCoors. But there are also 2,700-plus breweries—more than a third popping up in the last five years. Making higher-priced craft beers like hoppy pale ales, dark rich stouts and fringe flavours, these smaller producers are growing by double digits, from nothing to 7 percent of the total US market by volume and 12 percent by dollars spent. But there are only so many taps at the local bar, only so much shelf space in the supermarket aisle.
“It’s a grow or die mentality,” says Grossman in his low, unflappable voice. “If our brand isn’t growing, somebody else’s will. You can have a business model where you put the brakes on and only sell 30 cases of this really exotic, really expensive beer. But we’ve grown way past that.” Now that Sierra Nevada is the seventh-largest brewery in the country, with its signature Pale Ale sold in all 50 states, that’s not an option. Grossman is facing the same challenge that has stymied companies from Microsoft to General Motors: Once you’ve graduated from insurgent to incumbent, how do you keep growing—and keep the fan base happy?
Sierra Nevada’s answer is to stay close to its roots, constantly innovate and co-opt tiny competitors by partnering with them.
Growing up in the San Fernando Valley, Grossman developed the characteristics of a proto-entrepreneur—inventiveness bordering on larceny. He stole the motor of a neighbor’s lawn mower to build a go-kart, used a plastic explosives recipe to blow up every mailbox on the block and dropped homemade stink bombs in junior high. The day before his 12th birthday he was caught shoplifting circuit board clips from the local RadioShack.
Then he started channeling his creative urges toward photography, bike repair and (pre-legal drinking age) distilling.
Grossman met his future wife, Katie, while dabbling at Cal State Chico. He ultimately dropped out to manage a bike store, then opened a homebrewing supply shop. While that went nowhere, Grossman couldn’t shake the dream. “Bike shop I could do, but I’d probably be bored in a few years,” he says. “Brewery seemed a lot more fun.”
Riskier, too. He and partner Paul Camusi, a home-brew customer, sank all their savings (about $15,000) into Sierra Nevada, and turned to family and friends for $85,000 after banks said no. It took more than two years of grinding from start to production. In a prescient move they planned for a 10-barrel brewery, the size of Sierra’s current pilot brewery but many times larger than other home-brew-turned-commercial-startups then.
Grossman had to scrounge for parts, scavenging stainless steel tanks, pumps and piping from closed dairies and salvage yards across the West Coast. The old bottling system he bought proved useless. Katie, at home with their young daughter, questioned the whole venture, as Ken was spending 12-hour days doing the bulk of the welding and fabrication himself, while working a second job to provide a living. Brewing finally got started in November 1980, though the first 10 batches of pale ale were sacrificed producing something fit to drink.
“We were pretty confident we could sell 1,500 barrels a year,” says Grossman, with scant evidence for hope. But from bars in Chico to restaurants in San Francisco and eventually to distributors across the country, word spread about the new brewery’s intense flavours and commitment to quality ingredients—as in their refusal to use anything but whole cone hops. Barely profitable, the company built out production to 12,000 barrels a year by 1988. It also hired a few employees, including Steve Dresler, still head brewer 31 years later. (His description of the early work environment: “A very small group of creative, motivated people—and highly self-medicated. My first day I was putting bottles into boxes when everyone took their midmorning break to get stoned.”)
To handle growth Grossman oversaw the purchase and cross-Atlantic shipping of a 100-barrel copper brewhouse from a failed German company and installed it at a new Chico location in 1988. Four years later Sierra Nevada was pushing the limits of that system, which Grossman eventually built up to 300,000 barrels per year, five times the original intended capacity. Another expansion brought the site up to its current size, and since late 2012 the company’s production has once again been completely constrained, with revenues squeaking up only 2 percent in 2013. Grossman says the current round-the-clock factory pace isn’t sustainable with only one plant: “Historically we took a few weeks of every year to fix and rebuild. Last year we shut down for Christmas and Thanksgiving only.”
While multiple on-the-fly reconstruction jobs took their toll, problems festered. Grossman weathered a grueling five-year ownership battle with the less hands-on Camusi. Finally, in 1998, Grossman assumed undisclosed debt to buy out his 50/50 partner. In the aftermath Sierra Nevada cut back on innovation. By 2007 it had been 13 years since it released a new beer on a national scale and, as a result, lost market share as new microbrewers flooded in.
But Grossman, who admits he’s hands-on “to a fault”, was burned out and seriously explored a sale. Only the surprise enthusiasm of his three children to keep Sierra Nevada in the family stayed his hand. “I never got in it for the money, so if they want to have that legacy and carry it into the next generation, let’s make that happen,” he says. Today his oldest daughter, Sierra, runs the Torpedo Room, a bar in West Berkeley for sampling limited new releases. Youngest child Brian, 29, is overseeing a new East Coast brewery in Mills River, North Carolina. The plant—which the company says will ultimately cost well over $100 million—will open in August and slowly ramp up to 800,000 barrels per year, relieving pressure on Chico as well as slashing transportation expenses: Cross-country refrigerated shipping costs Sierra Nevada more than $4 per case.
With its 2,000 solar panels, the new plant is a showcase of green production—as distinctive to the company’s identity as the flavours of its brews. In Chico, where Grossman made environmental impact a top priority, 76 percent of electricity usage in 2013 was produced on-site, with 10,573 solar panels and four fuel cells; it recycles and composts 99.8 percent of its waste. Mirroring the home base, employees in Mills River will have a free day-care centre and health clinic.
All those good works couldn’t change the fact that the craft-beer revolution Grossman helped launch was passing him by. “If you walk down the grocery aisle and you get to beer, you say, ‘What’s wrong with this category?’” says Joe Whitney, head of sales and marketing. “There are hundreds of players, there’s all these flavours. It’s total chaos.” With almost no advertising, the signature citrus-and-pine blast of Sierra Nevada Pale Ale had become a reliable standby for millions, but consumers demanded ever more extreme flavours and styles, even willing to pay $12 for a single bottle.
So Grossman got busy, experimenting with new brews. Last year Sierra Nevada produced 55 new labels. Pale Ale is still the number one seller, accounting for 60 percent of the company’s sales. But the Torpedo Extra IPA, released in 2008 (and named for the giant device stuffed with hops that Grossman invented to add a flavour kick), generates 20 percent. Its 180,000 barrels last year makes it one of the most popular India pale ales in America. Seasonals have long been popular sellers for Sierra, but new ‘exotic’ brands like the Ovila Belgian-style brews and barrel-aged Bigfoot (with wine-like potency) have grown to 5 percent of the business in just a couple years.
Sierra Nevada is always compared with Boston Beer, its better-known, larger and publicly traded rival. Co-founder Jim Koch has had mixed results in diversifying from the now mainstream Sam Adams lager (which spent much of its first decade being produced by larger breweries). His Angry Orchard cider line is a hit in a lower-margin but fast-growth category. But the new Rebel IPA sparked fierce words in December from Lagunitas Brewing founder Tony Magee, who accused Boston Beer of imitating his hit IPA and of pressuring distributors to replace it on bar taps. Koch denied the charges, but the incident highlighted growing tension between small brewers and Boston Beer, which, at 3 million barrels a year and a $2.6 billion market cap, many now consider a craft brewer in name only.
By contrast, Grossman has grown through collaboration with smaller breweries, even at the expense of profit. Sierra Nevada will host a participatory “Beer Camp Across America” traveling festival this summer to highlight its place within the broader craft-beer movement. Dresler’s team has worked on the special-edition variety 12-pack, co-producing each beer with a different regional brewery, like Allagash, Russian River and Ninkasi. (“It’s incredible to be around someone who knows every single detail about what’s going on,” muses Jamie Floyd, Ninkasi’s founding brewer, on a recent visit to Grossman’s operations.) The project allows Sierra Nevada to trade in some of its operational know-how and national exposure for ties to younger, hipper brands.
“It’s hard to find many detractors of Sierra Nevada,” says Harry Schuhmacher, publisher of Beer Business Daily. “It’s so beloved and respected both in the industry and among consumers.” Grossman may be worth an estimated $800 million. But his challenge is keeping a good thing going in an industry where hype is as important as hops. As someone who jokes he’s in the alchemy business, he can’t afford to lose his golden recipe.
(This story appears in the 30 November, -0001 issue of Forbes India. To visit our Archives, click here.)





