
Women at work: Can we bridge the gender pay gap once and for all?
Income disparity is a result of systemic biases, socio-cultural norms, and low representation of women at the workplace, which companies can address by being more intentional about equity, and the government, through policy change
 Gender parity has become a steeper uphill battle in the wake of Covid-19, with the economic participation of women falling further
Image: Shutterstock
Gender parity has become a steeper uphill battle in the wake of Covid-19, with the economic participation of women falling further
Image: Shutterstock
On Twitter, the @PayGapApp is a bot account that calls out gender income disparities in companies listed on the UK government’s gender pay gap service database. On June 20, when technology company Tech Mahindra put out a tweet about LGBTQ+ inclusion, the account quote-tweeted it saying, “In this organisation, women’s median hourly pay is 1.2 percent lower than men’s.”
Since 2017, the UK has mandated public disclosures of average gender gaps between men and women for companies with 250 or more employees. Disclosures made by other Indian tech companies present in the UK indicate that on a median hourly basis, female employees in Infosys earn 0.7 percent less than their male counterparts, while the pay gap is 7.5 percent in Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) and 9 percent in Wipro.
In the US, on June 12, technology giant Google agreed to pay $118 million to settle (without admitting wrongdoing) a class action lawsuit that covers some 15,500 female employees in California. The suit was initiated by three former employees in 2017 who said the company had discriminated against women in pay and promotions, The Wall Street Journal reported, adding that Google placed women in “lower-job levels than similarly qualified males, leading to lower pay, and denied the women promotions or transitions to other teams that would have led to better career advancement.”
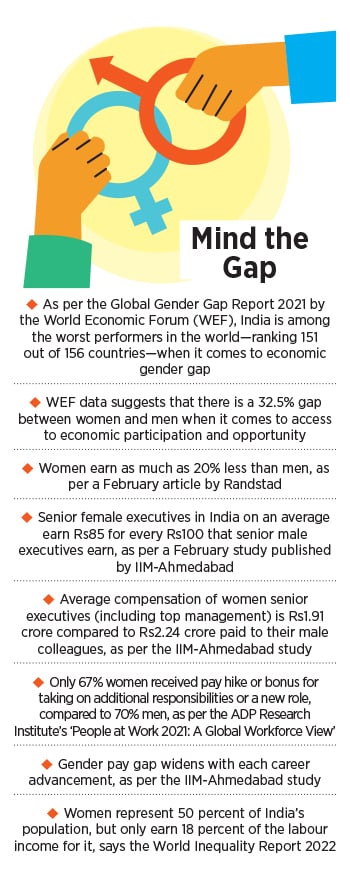
In India, an article in February by recruitment firm Randstad says that women earn as much as 20 percent less than men. A study published by IIM-Ahmedabad in the same month shows that senior female executives in India on an average earn Rs85 for every Rs100 that senior male executives earn. The research, based on responses from 109 out of 200 NSE companies with a sample size of over 4,000 executives for 2021, says women senior executives (including top management) earn an average compensation of Rs1.91 crore compared to Rs2.24 crore paid to their male colleagues.
Gender parity has become a steeper uphill battle in the wake of Covid-19, with the economic participation of women falling further. According to Azim Premji’s State of Working India Report in 2021, during the lockdown and the months after, 61 percent men remained employed compared to only 19 percent women, while just 7 percent men lost their jobs compared to 47 percent women. The World Inequality Report 2022 states that while women represent 50 percent of the population in India, they earn only 18 percent of the labour income for it.







 For example, says Sudhir Dhar, executive director-HR at Motilal Oswal Financial Services, the company has an internal community of female employees who are focussed on cultivating a network and support system for women to grow in the organisation. “The aim is for them to tell us what we can do as a company to help them grow within the organisation, so that more of them could rise to the higher level, even to the board.” He adds that hiring more women, particularly at senior levels, is also a priority.
For example, says Sudhir Dhar, executive director-HR at Motilal Oswal Financial Services, the company has an internal community of female employees who are focussed on cultivating a network and support system for women to grow in the organisation. “The aim is for them to tell us what we can do as a company to help them grow within the organisation, so that more of them could rise to the higher level, even to the board.” He adds that hiring more women, particularly at senior levels, is also a priority. 



