
Tull's Legendary sale may define Hollywood's future
Billionaire Thomas Tull is about to sell his comics-driven movie studio to China's richest man for a price rivalling what Disney paid for Lucasfilm. The result may be the future of Hollywood
While most of the US ground to a halt around Christmas, Thomas Tull, the billionaire founder of Legendary Entertainment, had never been busier. Or more stressed. He was smack in the middle of a deal to sell his studio to China’s richest man, Wang Jianlin, and his Dalian Wanda Group. But Christmas is just another day in China, and various hiccups stood in the way of Tull and a $3.5-billion cash-out.
Pacing the floors of his massive home in the tony Westlake Village complex just outside of Los Angeles, he first had to explain the deal to his consortium one by one, a varied bunch that ranged from institutional giants like Fidelity and Morgan Stanley and Japan’s SoftBank to individuals like billionaire venture capitalist Jim Breyer.
Then came the near-impossible task of minimising taxes on both sides—every shift in the terms invariably caused repercussions for one side or the other.
Finally Tull had to navigate the Chinese regulatory system, which forbids foreigners from owning stakes outright in entertainment companies—a problem, since Tull, who would continue in his CEO role, wanted to hold on to his 20 percent or so stake of Legendary. In the end, knowledgeable sources told Forbes, Tull likely had to make do with phantom stock, a China-friendly workaround that would mimic actual ownership, giving him a yearly payout plus 15 percent to 20 percent of the profit if the company is sold. (Legendary would not confirm this arrangement.)
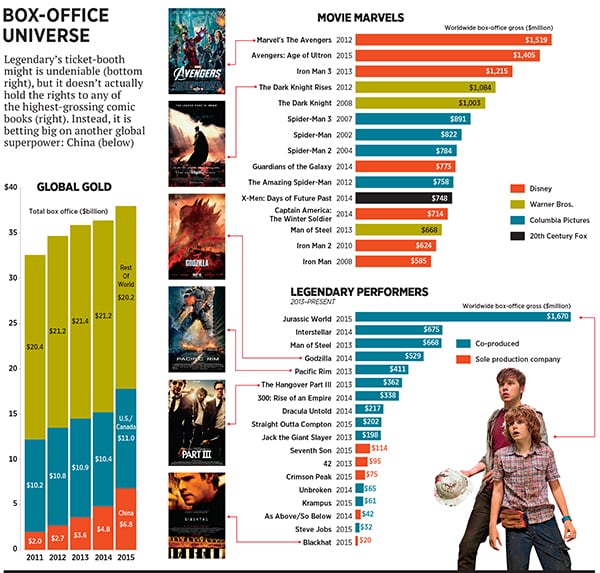
Such details were the culmination of a two-year process that started with a lunch at Wanda’s headquarters in Beijing in late 2013. Legendary, which has co-produced blockbusters such as The Dark Knight and Godzilla, had recently partnered with state-run China Film Group to develop movies in the country. He gained access to a burgeoning market—it will surpass the US next year as the world’s largest—and a near-sure distribution channel in a place that permits only 34 foreign films annually. The previous year Wang had snapped up US cinema chain AMC for $2.6 billion, taking the first step in what would become a string of international entertainment acquisitions to broaden the scope of his real estate conglomerate.
Almost immediately they began smoothing out personal differences—amid China’s culinary riches, Wang served Tull and his “very narrow palate” grilled chicken and salad—and basking in their similarities, including the fact that they grew up poor (albeit 7,000 miles apart). “I liked that there wasn’t a lot of flowery talk,” says the bread-and-butter Tull.
That lunch coincided with his forging of profitable partnerships (Tull’s humans-versus-monsters epic, Pacific Rim, pulled in 27 percent of its $411 million gross from China, much of it from Wanda’s theatres) and led to small investments, as Wang took a nearly 2 percent stake in Legendary. Then came more culinary courtesies: When Wang came to Los Angeles, it was Tull who sucked it up, taking China’s $29-billion man to a spicy Sichuan restaurant in the Century City Mall.
A positive dynamic had been set up. “At any business deal of size, it always seems like there are three moments that you feel like there’s just no way,” Tull recalls. Yet by New Year’s Eve Tull was able to call Wang with six fateful words: “I think we have a deal.”
That deal is expected to close imminently. And when it does it will mark several Hollywood milestones. Five of the six major studios—20th Century Fox, Warner Bros, Paramount, Disney and Universal—have scored investment from China or formed joint ventures overseas in the last 18 months, but this will be the first complete buyout of an American movie studio. “Legendary is a gateway to cultural and financial alignment between the Hollywood moviemaking world and the rapidly expanding Chinese marketplace,” Wang says.
Second, it will show that the comics-driven blockbuster formula can yield profitable exits even for companies that aren’t named Marvel or DC. Third, it would validate the data-based Moneyball strategy that has been all the rage in Hollywood over the past decade but has looked rather stupid lately.
The sale would also be a stunning triumph of dealmaking for the 45-year-old Tull. Disney paid $4.1 billion for Lucasfilm and the mighty Star Wars franchise and another $4 billion for Marvel and a character universe—the Hulk, Thor and Captain America—that collectively is the highest-grossing franchise of all time. What does Wang’s $3.5 billion, which includes some $900 million in debt, buy him?
“It’s not exactly clear what they are paying for, even at a premium valuation,” said Dan Clivner, a Los Angeles-based partner at law firm Sidley Austin who specialises in mergers and acquisitions.
Legendary uses its money and production savvy to produce other people’s franchises: Most of its biggest hits, whether The Hangover or Jurassic World, have been jointly produced with Warner Bros or Universal, its most recent distribution partner, using intellectual property they own. It has had some success licensing properties—Godzilla is licensed from Toho—but that can’t justify the valuation, either. Legendary boasts about the content it owns, but there’s no way Pacific Rim, along with a small horror movie and three disappointments, can almost equal the value of Star Wars. Not even close.
Ultimately Wang seems willing to vastly overpay to get a controlling stake in a Hollywood entity, no small feat. China’s second-richest man, Jack Ma, sources tell Forbes, has repeatedly been thwarted in his efforts to take over Paramount and other studios, versus making a minority investment. (His Alibaba Pictures co-financed Paramount’s Mission: Impossible—Rogue Nation last year.)
Wang is also betting on Tull himself. Rather than follow the century-old tradition of Hollywood-insider fleecing starry-eyed outsider, Tull won’t cash out anything from the deal. While his investors will do magnificently, Tull is sticking with his phantom stock—he’s betting on the future, on the same side as Wang. With Legendary at the centre of seemingly every major movie business trend, understanding what Tull has built, and where he’s going, provides an insightful microcosm of the future of Hollywood itself.
Hollywood’s global mogul was raised by a single mom outside Binghamton, New York. Tull, who helped support two younger sisters by mowing lawns in the summer and shovelling snow in the winter, sought escape in fantasy and science fiction: Tolkien’s Lord of the Rings trilogy and Dune were among his childhood favourites.
Tull mixed sports with his nerdy reading habits, landing a football scholarship to tiny Hamilton College in upstate New York. It was here that he read Frank Miller’s The Dark Knight Returns and The Watchmen, the latter of which Legendary would someday co-produce. And he continued to be entrepreneurial, selling T-shirts and signing up local businesses for ads in a directory he distributed to students.
Tull considered law school but was deterred by potential debt. So at 23 he started a chain of local laundries, called Smart Wash. Tull’s twist: A computerised system that allowed him to flex the price of washes to attract customers during slow periods and maximise revenue during the Sunday rush.
“I’ve always known that I had to work for myself or at least have my own business,” says Tull, who at 6 feet, with a squat head that disappears into his broad shoulders, still looks like a big-target wide receiver (in 2008, he fulfilled a childhood dream by buying a small stake in the Pittsburgh Steelers). “Struggling as a family financially, I grew up within the confines of constantly worrying [whether] the light is going to get turned off. I think you can get drive from that.”
That drive was industry-blind. In 1995 he moved from laundries to tax prep, rolling up 500 Jackson Hewitt franchises. Then came tech ahead of the original dot-com bubble, scouting deals for venture firm Southeast Interactive.
By 2001 he had moved on to media, joining a small Atlanta investment company, Convex Group, and working his way up to president. He soon started thinking about Hollywood. “It was the largest business I was aware of as an asset class or category that had no professional capital,” Tull recalls. “Then I read that it was our country’s second-biggest export.”
Tull hired a data firm to gather years of information on film performances. After looking at the results, he figured that with enough capital it wouldn’t be hard to build a film library—and a scalable business.
With great fanfare Relativity Media was simultaneously pursuing an algorithmically driven sweet spot of formulaic $30-million movies, anchored by a recognisable star and guaranteed foreign distribution.
Tull went the other direction. The sci-fi geek, whose Legendary office is strewn with comic books, deduced it was the $100 million-plus tentpole, fixed to a known franchise, that was the least risky. Tull also examined international growth numbers and saw a remarkable upward trend. Coupled with attractive margins in the DVD business at the time, blockbuster financing began to make financial sense.
Tull talked his way into a meeting with Warner Bros, which provided the infrastructure to distribute and market films globally that a newcomer like Tull could not do. A deal template emerged: Legendary would co-finance and co-produce 25 films it cherry-picked from the Warner Bros slate, vouching for approximately 50 percent of each movie’s budget. This provided Warner Bros with capital and offset the risk of expensive films that could affect quarterly earnings. Legendary would also pay Warner Bros an estimated 10 percent distribution fee. In exchange Warner Bros and Legendary would then share any profits proportionally.
A good hedge for Warner Bros provided a great opportunity for a Hollywood neophyte. All he was missing was the money. “The most difficult experience of my career, of my life by far, was raising the initial capital,” says Tull of the year he spent attempting to gather the $500 million he had pledged. Horror stories of screwy Hollywood accounting and investors who had lost money on movies preceded him. “The meetings lasted about 15 minutes on average, in which they’d say, ‘No way in hell. You can take a beverage on the way out’. ”
After what Tull calls an “impassioned” final plea to a small round of investors and a commitment to invest his own money, coupled with a credit line from JPMorgan, Legendary in late 2004 managed to score startup cash from ABRY Partners, Bank of America, M/C Partners and Columbia Capital.
They were taking a risk. When blockbusters work, they gross over $1 billion, spawn sequels and score millions more in merchandising and theme park tickets When they don’t, it’s an expensive bomb that can ruin a balance sheet. Legendary quickly went on a winning streak, starting with Batman Begins and 300. Eventually it was putting up 50 percent of the budget for 50 percent of profits on movies like The Dark Knight Rises, which grossed $1.1 billion on a $250-million budget, and then taking a 75 percent stake on movies such as Godzilla, which tallied $529 million on a $160 million price tag. Global results were always top-of-mind. The nonstop action and infrequent dialogue in most Legendary blockbusters help them perform remarkably well overseas, particularly in China, where fewer words mean fewer reasons to upset the censors.
Part of Tull’s secret sauce was analytics. But whereas Ryan Kavanaugh and his Relativity Media, the other Moneyball upstart backed by Wall Street cash, swung for singles, claiming its computers could predict failure or success based on plotlines, genres, stars and release dates, Tull went for the fences and leveraged his data to affect things within his control. Specifically, determining how he could shave costs and boost audiences on blockbusters, where the marketing budget often approaches production costs.
Legendary says that even before a movie has the green light it compiles customer profiles to find audiences who are at least 40 percent likely to see a film and advertises only to them using cheaper digital ads. Boasts Tull: “We went live on Godzilla and spent less money on marketing than we were slated to. We opened $35 million higher than tracking had us [at].”
By using aggregated social media sentiment to hone its targeting, Tull claims he can shave 15 percent to 20 percent off his marketing costs, which often translates into eight figures per picture.
By 2013 an emboldened Tull moved Legendary into completely producing—and owning—its own films, drawing in the likes of venture capital heavyweight and early Facebook investor Jim Breyer, who served on the board of Marvel and invested more than $100 million in Legendary through separate vehicles, including personal funds. Says Breyer: “Thomas had an incredibly long-term view of the business and a passion for how analytics and technology can help leverage what has been a chronically high-fixed-cost-structure business.”
But owning properties forced him to shift from his comic book tentpoles—and the results showed. Legendary’s five solo films include three stinkers. After a so-so debut with Jackie Robinson biopic 42, the fantasy Seventh Son tallied $114.1 million on a $95-million budget. Blackhat, a 2015 crime thriller, grossed $20 million on a $70-million budget, while the Guillermo del Toro-directed Crimson Peak grossed $74.7 million on a $55-million budget. (The middle two are conveniently absent from Legendary’s website library.) Its biggest independent hit was its second release, As Above/So Below, a horror film that grossed $41.9 million on a $5- million budget. Considering theatres pocket approximately 50 percent of box office receipts, the Legendary slate has performed quite poorly. “It’s very hard to build a new thing,” says Tull.
Relativity Media discovered that the hard way, as Kavanaugh’s data sets couldn’t prevent flop after self-financed flop—or a high-profile trip to corporate bankruptcy that has been Hollywood’s most buzzed-about soap opera over the past eight months. Tull’s bigger co-financed winners (Jurassic World alone likely made Legendary $200 million) and smaller roster of flops allowed him to avoid that fate. And his nerdy competence—and China focus—contrasts well with Kavanaugh’s bluster. That goes a long way to explaining the $3.5-billion difference. Calling Tull “the perfect partner”, Wang says: “Together we can open doors for new talent, stories and audiences to come together in this new world.”
Tull got a glimpse of Legendary’s future last June when he visited Qingdao, a coastal city halfway between Shanghai and Beijing. There Wang is building the world’s largest film studio, an $8.2 billion property that sprawls across 494 acres and is set to open in 2018.
Such massive investments have the blessing of the powerful Chinese government. China’s former leader Hu Jintao publicly discussed using culture “as part of the soft power of our country”. And Hu specifically meant culture “not as cultural exchange or awareness but as a business,” says Dominic Ng, chairman and CEO of East West Bank. “The Chinese government feels strongly that in order to portray a better image, they need the entertainment business—the culture business—to get stronger.” According to a New York Times expose last year, Wanda has close ties to senior Communist Party leaders; Wang denies the connections.
Wang’s holdings also include Wanda Cinema Line, one of China’s largest movie theatre chains, and Hoyts, an Australian cinema group. “Wanda is trying to create a global, vertically-integrated motion picture company,” says Gordon Crawford, a retired investor who put money into Legendary in 2012. “To do that [Wang] needs the capability to make tentpole movies that play globally.”
The first full-blown Wanda/Legendary co-production will test that in a major way. Even as the Wanda studio is being finished in Qingdao, filming is under way there for The Great Wall. Shot entirely in China, the $135-million fantasy-adventure film is helmed by Chinese director Zhang Yimou and stars both a US lead (Matt Damon) and a Hong Kong heartthrob (Andy Lau).
The story, about an army making a last stand for humanity against aliens on the Great Wall, came courtesy of Tull, who typed up an outline six years ago, before bringing in World War Z writer Max Brooks to polish the story.
“As a kid I remember reading that the only man-made object that you can see from space was the Great Wall,” Tull recalls. “I remember thinking, what would compel these people to build something that audacious? Then, of course, because I have a geeky sensibility, it was like well, what would they build to keep out?”
Though Legendary is co-producing the movie with China Film Group and China’s Le Vision Pictures and sharing financing with others, it’s an expensive bet for an unproven hybrid. Forbes estimates it will have to gross at least $350-million worldwide to break even; Monster Hunt became China’s top-grossing film ever last year with $391 million.
That’s just the beginning. Tull plans to develop his own movies and licence still more high-profile properties, including Warcraft, licensed from the Activision Blizzard videogame; Hot Wheels, licensed from toymaker Mattel; Mass Effect, licensed from the BioWare shoot- ’em-up game; plus three more films in a King Kong and Godzilla “monster-verse”. Along with a small TV business and virtual reality wing, Legendary has launched its own comic book publishers to source movies; it recently issued a graphic novel tie-in to 2015’s Krampus, but a bestseller has yet to appear.
And with Disney opening a $5.5-billion theme park in Shanghai in June, with Universal Studios a few years behind it in Beijing, Wang says he has theme park aspirations for his new properties.
Taken together, there’s the potential for major studio scope, albeit one where the Qingdao facility is as important as Legendary’s office in Burbank. Let it be noted: Tull is taking Mandarin lessons.
(This story appears in the 30 November, -0001 issue of Forbes India. To visit our Archives, click here.)






