Protect India's tigers, it's good for climate: study
By AFPRelaxnews | May 29, 2023
Tigers are an "umbrella species", which means that by protecting them we also protect the forests they live in, which are home to an incredible diversity of wildlife
 [CAPTION]
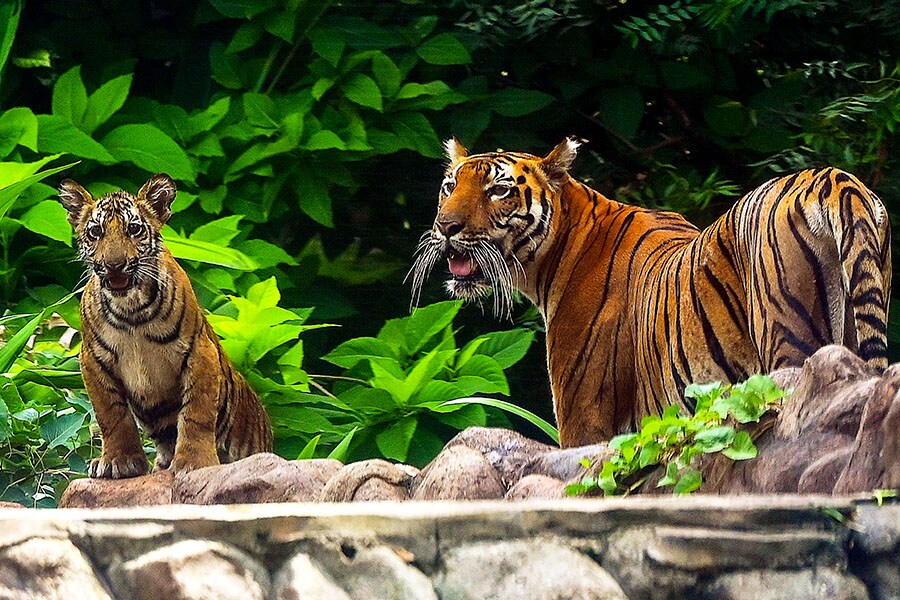
Three-quarters of the world's wild tigers live in India, but the destruction of their natural habitat have seen their numbers plummet.
Image: Sujit Jaiswal/ AFP [/CAPTION]
[CAPTION]
Three-quarters of the world's wild tigers live in India, but the destruction of their natural habitat have seen their numbers plummet.
Image: Sujit Jaiswal/ AFP [/CAPTION]
India's efforts to protect its endangered tigers have inadvertently helped avoid a large amount of climate change-causing carbon emissions by preventing deforestation, a study said on Thursday.
Three-quarters of the world's wild tigers live in India, but the destruction of their natural habitat have seen their numbers plummet.
The number of tigers roaming the country's forests fell from 40,000 when India gained independence in 1947 to just 1,500 in 2006.
_RSS_However their number rose above 3,000 this year, according to the latest official figures.
To help their numbers rebound, India has designated 52 tiger reserves where logging and deforestation are heavily regulated.
Aakash Lamba, a researcher at the National University of Singapore and the new study's lead author, told AFP that tigers are an "umbrella species".
This "means that by protecting them we also protect the forests they live in, which are home to an incredible diversity of wildlife," he told AFP.
Forests are a "carbon sink", which mean they absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere than they release, making them a crucial tool in the fight against climate change.
India, the world's third largest emitter of greenhouse gases, has pledged to lower its emissions.
Also read: Some animals could play a key role in fighting global warming
Million metric tons
Lamba, who grew up in India, said the team of researchers sought to establish an empirical link between tiger conservation and carbon emissions.They compared the rate of deforestation in the special tiger reserves to areas where the big cats also live, but are less strictly protected.
More than 61,000 hectares of forest was lost across 162 different areas between 2001 and 2020, according to the study.
More than three quarters of the deforestation was in areas outside of the tiger reserves.
Inside the tiger reserves, almost 6,000 hectares was saved from deforestation between 2007 to 2020. That equates to more than a million metric tons of carbon emissions avoided, the study estimated.
Lamba emphasised the economic impact of those saved emissions in a country that has been hit hard by the effects of climate change—particularly the agricultural industry.
Taking into account the social cost of those emissions, more than $92 million had been saved, the researchers calculated.
If counted as part of an carbon offset scheme, the avoided deforestation amounted to more than $6 million, they added.
"The financial benefits of avoiding carbon emissions are more than a quarter of the annual expenditure on tiger conservation in India," Lamba said.
"This significant outcome highlights how investments in wildlife conservation not only safeguard ecosystems and wildlife but also benefit societies and economies."
The study was published in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution.
The findings come after a study published in March suggested protecting or restoring a handful of wild animals such as whales, wolves and otters could help capture 6.4 billion tons of carbon dioxide every year.